Publication
GeFL: Model-Agnostic Federated Learning with Generative Models
Honggu Kang*, Seohyeon Cha*, Jiwan Seo, and Joonhyuk Kang (* Equal Contribution)IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing
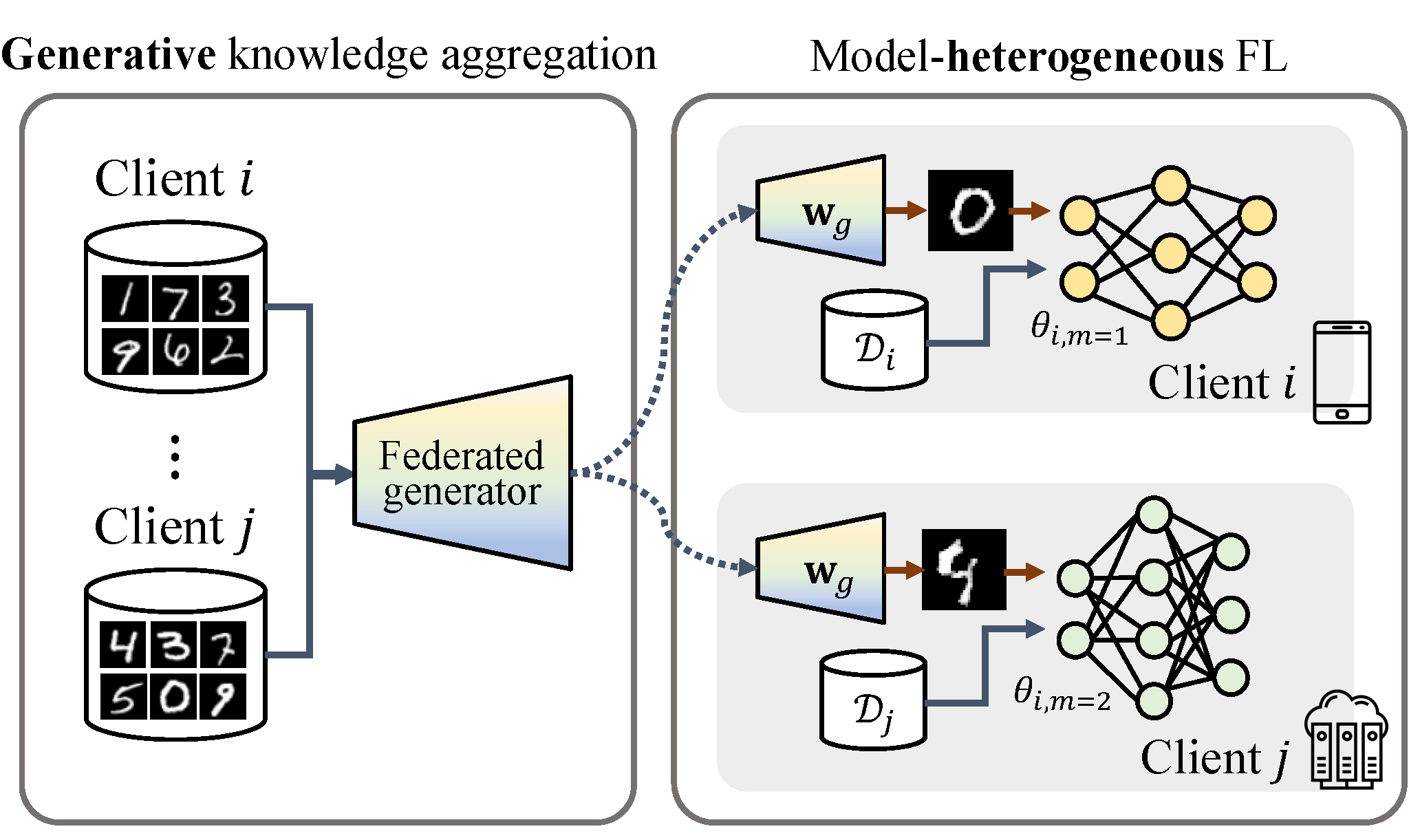
Federated learning (FL) is a promising paradigm in distributed learning while preserving the privacy of users. However, the increasing size of recent models makes it unaffordable for a few users to encompass the model. It leads the users to adopt heterogeneous models based on their diverse computing capabilities and network bandwidth. Correspondingly, FL with heterogeneous models should be addressed, given that FL typically involves training a single global model. In this paper, we propose Generative Model-Aided Federated Learning (GeFL), incorporating a generative model which aggregates global knowledge across users of heterogeneous models. Our experiments on various classification tasks demonstrate the notable performance improvements of GeFL compared to baselines, as well as limitations in terms of privacy and scalability. To tackle these concerns, we introduce a novel framework, GeFL-F. It trains target networks aided by feature-generative models. We empirically demonstrate the consistent performance gains of GeFL-F, while proving better privacy preservation and robustness to a large number of clients.
On the Temperature of Bayesian Graph Neural Networks for Conformal Prediction
Seohyeon Cha, Honggu Kang, and Joonhyuk KangNeurIPS 2023 New Frontiers in Graph Learning Workshop (NeurIPS GLFrontiers 2023)
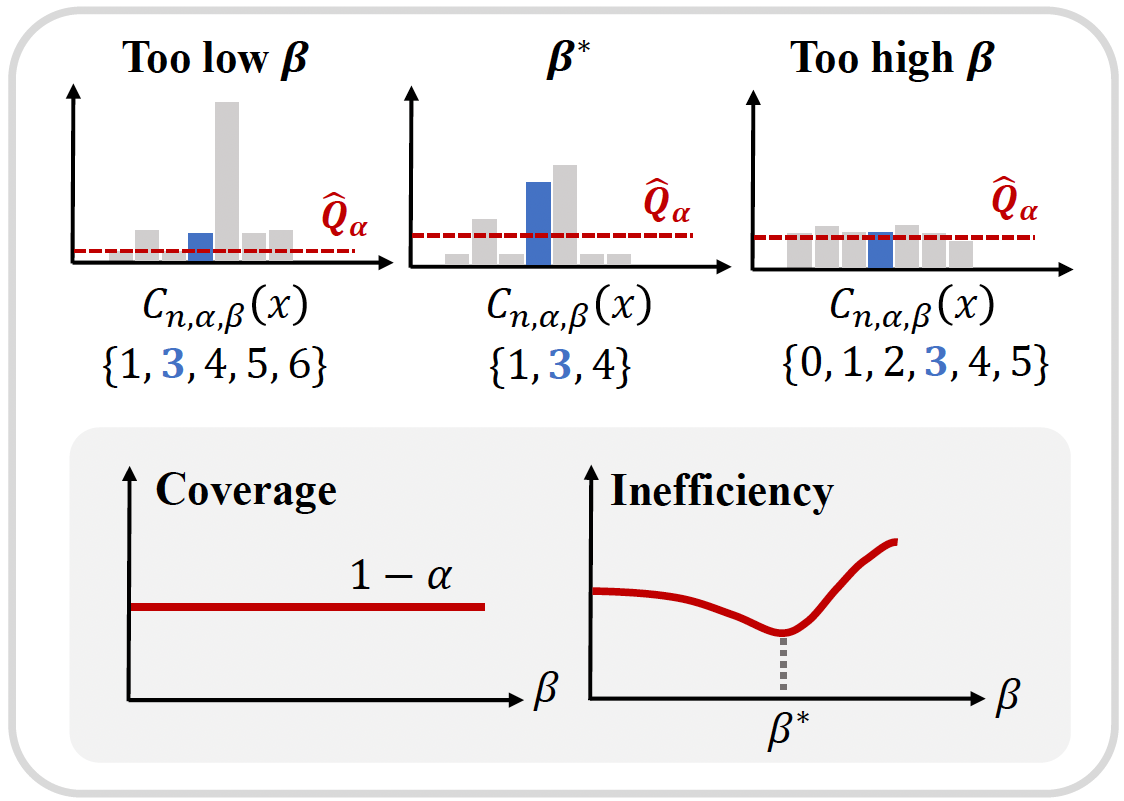
Accurate uncertainty quantification in graph neural networks (GNNs) is essential, especially in high-stakes domains where GNNs are frequently employed. Conformal prediction (CP) offers a promising framework for quantifying uncertainty by providing valid prediction sets for any black-box model. CP ensures formal probabilistic guarantees that a prediction set contains a true label with a desired probability. However, the size of prediction sets, known as inefficiency, is influenced by the underlying model and data generating process. On the other hand, Bayesian learning also provides a credible region based on the estimated posterior distribution, but this region is well-calibrated only when the model is correctly specified. Building on a recent work that introduced a scaling parameter for constructing valid credible regions from posterior estimate, our study explores the advantages of incorporating a temperature parameter into Bayesian GNNs within CP framework. We empirically demonstrate the existence of temperatures that result in more efficient prediction sets. Furthermore, we conduct an analysis to identify the factors contributing to inefficiency and offer valuable insights into the relationship between CP performance and model calibration.
NeFL: Nested Model Scaling for Federated Learning with System Heterogeneous Clients
Honggu Kang, Seohyeon Cha, Jinwoo Shin, Jongmyeong Lee, and Joonhyuk KangIEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing
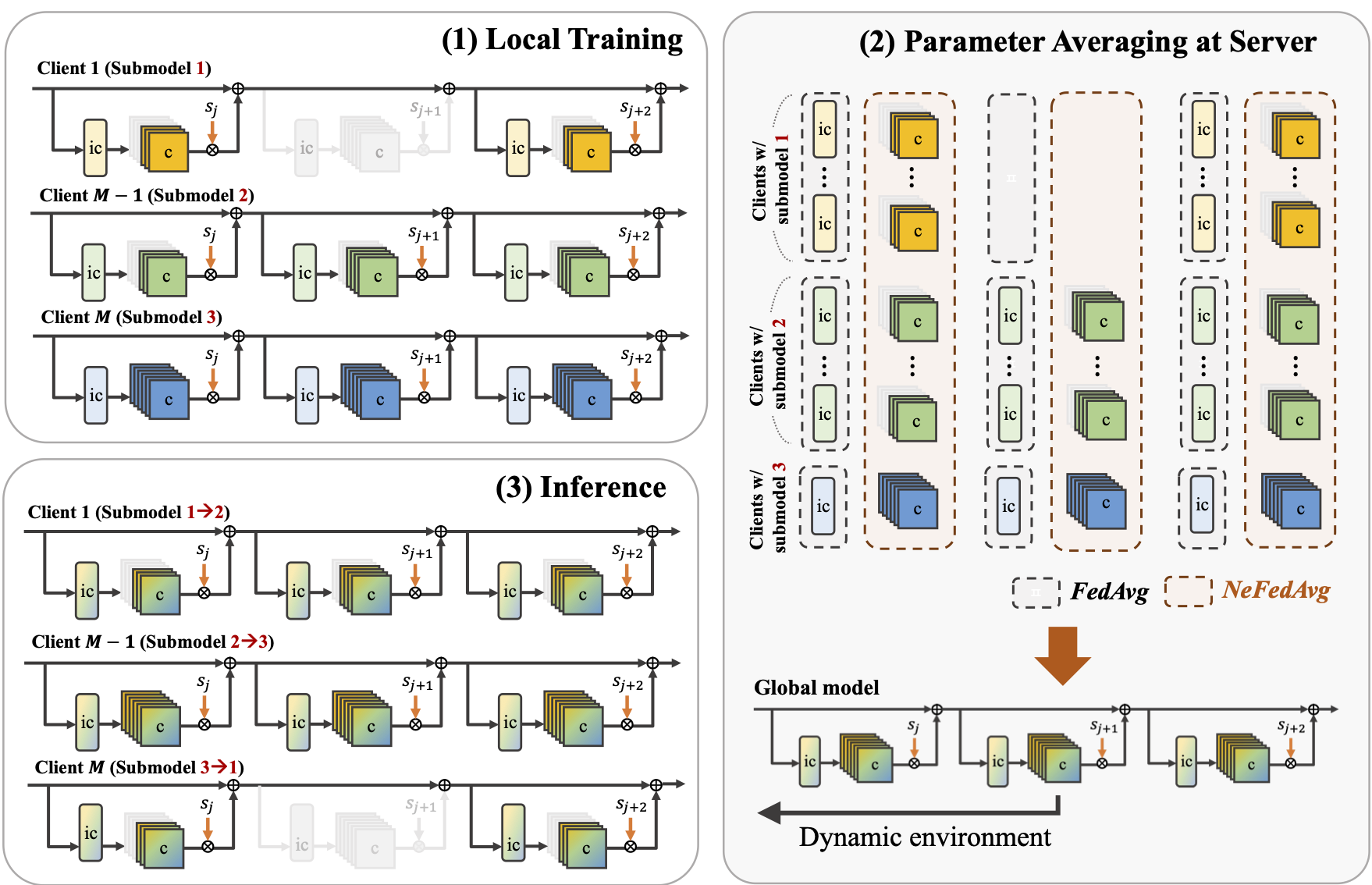
Federated learning (FL) enables distributed training while preserving data privacy, but stragglers—slow or incapable clients—can significantly slow down the total training time and degrade performance. To mitigate the impact of stragglers, system heterogeneity, including heterogeneous computing and network bandwidth, has been addressed. While previous studies have addressed system heterogeneity by splitting models into submodels, they offer limited flexibility in model architecture design, without considering potential inconsistencies arising from training multiple submodel architectures. We propose nested federated learning (NeFL), a generalized framework that efficiently divides deep neural networks into submodels using both depthwise and widthwise scaling. NeFL interprets forward propagation as solving ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with adaptive step sizes, allowing for dynamic submodel architectures. To address the inconsistency arising from training multiple submodel architectures, NeFL decouples a subset of parameters from those being trained for each submodel. An averaging method is proposed to handle these decoupled parameters during aggregation. NeFL enables resource-constrained devices to effectively participate in the FL pipeline, facilitating larger datasets for model training. Experiments demonstrate that NeFL achieves performance gain, especially for the worst-case submodel compared to baseline approaches. Furthermore, NeFL aligns with recent advances in FL, such as leveraging pre-trained models and accounting for statistical heterogeneity.
Intelligent Surface-aided Transmit-array Antenna in mmWave Communication System with Historical Channel Observation
Seohyeon Cha, Sanghyuk Kim, Jiwan Seo, and Joonhyuk KangIn IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), 2022.
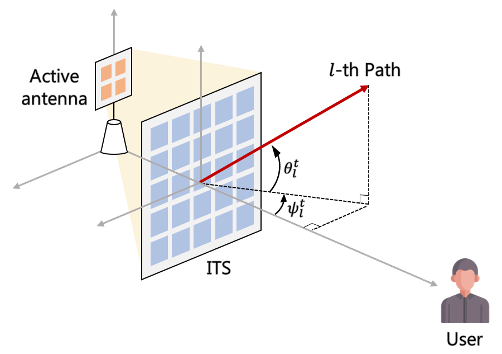
In this paper, we study an intelligent surface-aided transmit-array antenna architecture which deploys intelligent transmitting surface (ITS) near the active antenna in mmWave downlink communication system. We aim to maximize the average achievable rate at the user by optimizing the phase shift matrix of ITS. To overcome the difficulty of acquiring channel state information (CSI), we propose a stochastic gradient descent (SGD)-based algorithm that requires only historical channel observations. Simulation results show that our proposed scheme with single active antenna and ITS outperforms conventional MISO system.